Microplastics, plastic particles with a size < 5 mm, are emerging pollutants in marine environment and have attracted growing attention in recent years. Microplastics are known to pervade the global marine ecosystem. Owing to their resistance to chemical, photochemical and mechanical degradation as well as biodegradation, microplastics can accumulate in the ocean for long periods of time. Additionally, due to their small size, microplastics can be readily ingested by marine organisms across all trophic levels, causing direct physical damages. Importantly, microplastics induced indirect toxicity to marine organism through adsorbed chemical pollutants and released plastic additive. However, the effects of microplastics in marine environments is not well understood. Therefore, it is urgent to investigate the microplastic pollution in mariculture farm, the impact of mariculture-derived microplastics on bacterial biofilm, and the combined toxicity of microplastics with other pollutants to marine organisms.
Recently, under the support of National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0900703) and the Youth Talent Support Program of the Laboratory for Marine Ecology and Environmental Science, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao) (LMEES-YTSP-2018-04-01), Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute (YSFRI), CAFS has achieved the important progress in effects of microplastics in marine environments as following:
(1) Polystyrene microplastics acted both as a carrier and scavenger for the bioaccumulation of BDE-209. Importantly, the carrier role of microplastics was greater than scavenger one. Microplastics increased the negative effect of BDE-209 (100 μg/L) on hemocyte phagocytosis, and ultrastructural changes in gills and digestive gland of scallops due to their carrier role for the bioaccumulation of BDE-209. However, microplastics did not increase the DNA damage of BDE-209 on the hemocytes. These findings are evidence of microplastics transferring adsorbed pollutants to marine organisms, and increasing their toxicity. (Xia et al., 2020, Environmental Pollution)
(2) Average abundance of microplastics in the surface sediments of Sanggou Bay was 1674 ± 526 items/kg dry weight, which represented a heavy level when compared with other sea areas, including coastal waters, estuaries, the open sea and other mariculture areas. Microplastics with a size of <0.5 mm were dominant throughout four seasons. The dominant shape of microplastics was granule in summer, autumn and winter, and film in spring, respectively. The most common color of microplastics was transparent. Polyethylene was the dominant polymer in summer, autumn, and winter, while polystyrene accounted for the largest proportion in spring. Approximately 57.72% of the microplastics in surface sediments originated from the plastic mariculture facilities, suggesting that mariculture makes a signi?cant contribution to microplastic pollution in Sanggou Bay. Estimated inventory of microplastics in surface sediments of Sanggou Bay was 183.73 tons. Our results improve the understanding of risks caused by mariculture-derived microplastics to marine ecosystem and human health. (Sui et al., 2020, Science of the Total Environment)
(3) Bacterial communities on microplastics mainly originated from their surrounding seawater and sediment, with an average contribution on total microplastics adherent population of 47.91% and 37.33%, respectively. Principle coordinate analysis showed that community similarity between microplastics and surrounding seawater decreased with exposure time. In addition, lower average bacterial community diversity and higher relative abundances of bacteria from the genera Vibrio, Pseudoalteromonas and Alteromonas on microplastics than those in their surrounding seawater and sediments indicated that microplastics might enrich potential pathogens and bacteria related with carbohydrate metabolism. They are responsible for the signi?cant differences in KEGG Orthology pathways (infectious disease and carbohydrate metabolism) between microplastics and seawater. The KO pathway (Infectious Diseases) associated with MPs was also signi?cantly higher than those with feathers in the nearshore area. Microplastics might be vectors for enrichment of potentially pathogenic Vibrio, and enhance the ecological risk of microplastics to mariculture industry. (Sun et al., 2020, Environmental Pollution)
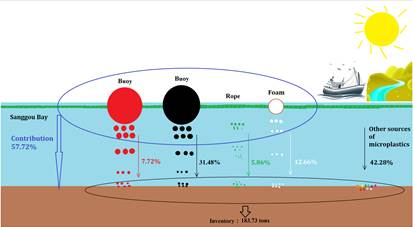
Spatiotemporal distribution, source identification and inventory of microplastics in surface sediments from Sanggou Bay
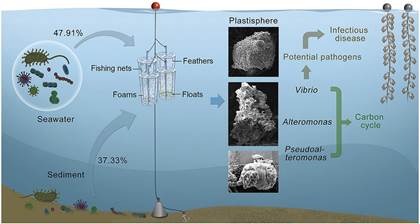
Impact of mariculture-derived microplastics on bacterial biofilm formation
1. Xia, B., Zhang, J., Zhao, X., Feng, J., Teng, Y., Chen, B., Sun, X., Zhu, L., Sun, X., Qu, K., 2019. Polystyrene microplastics increase uptake, elimination and cytotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the marine scallop Chlamys farreri. Environ. Pollut. 258, 113657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113657
2. Sui, Q., Zhang, L., Xia, B., Chen, B., Sun, X., Zhu, L., Wang, R., Qu, K., 2020. Spatiotemporal distribution, source identification and inventory of microplastics in surface sediments from Sanggou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 723, 138064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138064
3. Sun, X., Chen, B., Xia, B., Li, Q., Zhu, L., Zhao, X., Gao, Y., Qu, K., 2020. Impact of mariculture-derived microplastics on bacterial biofilm formation and their potential threat to mariculture: A case in situ study on the Sungo Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 262, 114336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114336
